history of computer network
The history of computer networks is vast, so we will discuss different generations of computer networks according to their timeline
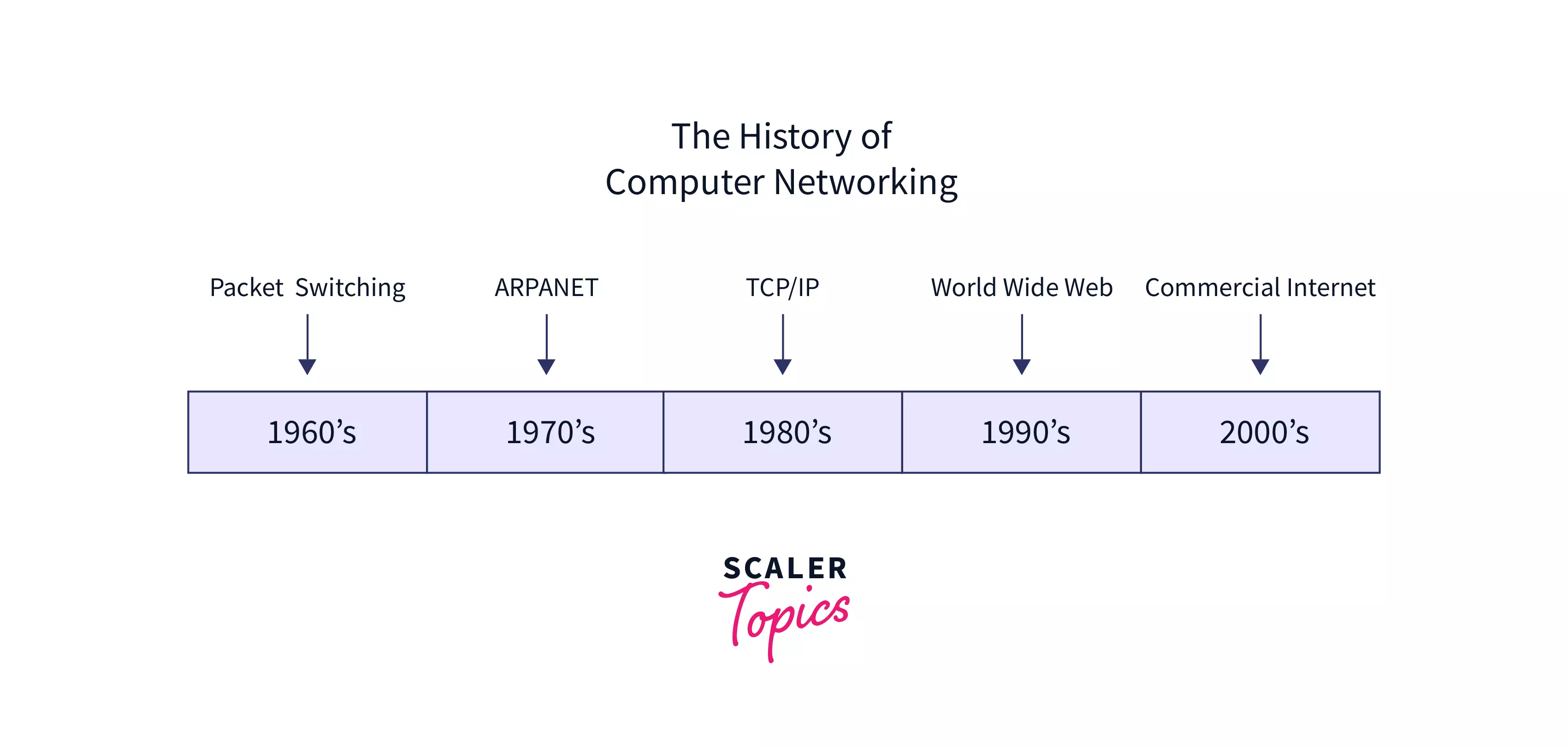
- In his paper "Information Flow in Large Communication Nets", Leonard Kleinrock introduced the notion of ARPANET (one of the early computer networks) in 1961. The telephone network was the most powerful network on the planet at the time. The telephone network transmits data from a sender to a receiver using circuit switching, which is a suitable choice given that voice is transferred at a consistent pace between sender and receiver.
- Leonard Kleinrock published the first work on packet switching methods. Kleinrock's work neatly illustrated the efficiency of the packet-switching strategy employing queuing theory for busy traffic sources. At the same time, Paul Baran began researching the use of packet switching for secure voice-over military networks at the Rand Institute.
- In 1969, the first packet-switched computer network and a direct ancestor of today's public internet ARPANET was first used. It was the first to use the TCP/IP protocol suite, which later evolved into the internet. The Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), a US Department of Defence division, developed ARPANET. ARPANET initially had four nodes, i.e., the University of California at Los Angeles (UCLA), Stanford Research Institute (SRI), University of California at Santa Barbara (UCSB), and the University of Utah. The first communication between UCLA and SRI took place on October 29, 1969
Roy Tomlinson invented email after UCLA was connected to Bolt Beranek and
Newman, Inc. (BBN) in 197
History of Computer Network | Scaler Topics
https://youtu.be/N5LjE77IHmk
تعليقات
إرسال تعليق